প্রদত্ত ডেটা পয়েন্টের বিচ্ছিন্ন সেটের মধ্যে নতুন ডেটা পয়েন্ট তৈরি করার জন্য, ইন্টারপোলেশন কৌশল ব্যবহার করা হয়। ল্যাগ্রঞ্জ ইন্টারপোলেশন কৌশল তাদের মধ্যে একটি। যখন প্রদত্ত ডেটা পয়েন্টগুলি সমানভাবে বিতরণ করা হয় না, তখন আমরা সমাধানটি খুঁজে পেতে এই ইন্টারপোলেশন পদ্ধতিটি ব্যবহার করতে পারি। ল্যাগ্রেঞ্জ ইন্টারপোলেশনের জন্য, আমাদের এই সমীকরণটি অনুসরণ করতে হবে।
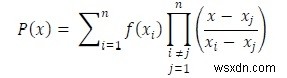
ইনপুট এবং আউটপুট
Input:
List of x and f(x) values. find f(3.25)
x: {0,1,2,3,4,5,6}
f(x): {0,1,8,27,64,125,216}
Output:
Result after Lagrange interpolation f(3.25) = 34.3281 অ্যালগরিদম
largrangeInterpolation(x: array, fx: array, x1)
ইনপুট - পূর্বে পরিচিত ডেটা পাওয়ার জন্য x অ্যারে এবং fx অ্যারে, এবং পয়েন্ট x1।
আউটপুট: f(x1) এর মান।
Begin res := 0 and tempSum := 0 for i := 1 to n, do tempProd := 1 for j := 1 to n, do if i ≠ j, then tempProf := tempProd * (x1 – x[j])/(x[i] – x[j]) done tempPord := tempProd * fx[i] res := res + tempProd done return res End
উদাহরণ
#include<iostream>
#define N 6
using namespace std;
double lagrange(double x[], double fx[], double x1) {
double res = 0, tempSum = 0;
for(int i = 1; i<=N; i++) {
double tempProd = 1; //for each iteration initialize temp product
for(int j = 1; j<=N; j++) {
if(i != j) { //if i = j, then denominator will be 0
tempProd *= (x1 - x[j])/(x[i] - x[j]); //multiply each term using formula
}
}
tempProd *= fx[i]; //multiply f(xi)
res += tempProd;
}
return res;
}
main() {
double x[N+1] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6};
double y[N+1] = {0,1,8,27,64,125,216};
double x1 = 3.25;
cout << "Result after lagrange interpolation f("<<x1<<") = " << lagrange(x, y, x1);
} আউটপুট
Result after lagrange interpolation f(3.25) = 34.3281


