একটি সংযুক্ত গ্রাফ রয়েছে G(V,E) এবং প্রতিটি প্রান্তের ওজন বা খরচ দেওয়া আছে। ক্রুসকালের অ্যালগরিদম গ্রাফ এবং খরচ ব্যবহার করে ন্যূনতম স্প্যানিং ট্রি খুঁজে বের করবে।
এটা একত্রীকরণ গাছ পদ্ধতি. প্রাথমিকভাবে বিভিন্ন গাছ আছে, এই অ্যালগরিদম সেগুলিকে একত্রিত করবে সেই প্রান্তগুলি নিয়ে যার খরচ সর্বনিম্ন, এবং একটি একক গাছ তৈরি করবে৷
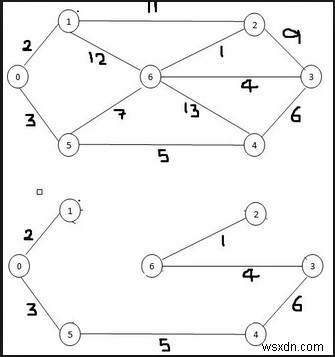
এই সমস্যায়, সমস্ত প্রান্ত তালিকাভুক্ত করা হয়েছে, এবং তাদের খরচের উপর ভিত্তি করে সাজানো হয়েছে। তালিকা থেকে, ন্যূনতম খরচ সহ প্রান্তগুলি বের করে গাছে যোগ করা হয়, এবং প্রতিটি প্রান্ত তৈরির চক্রটি কিনা তা পরীক্ষা করা হয়, যদি এটি একটি চক্র তৈরি করে তবে তালিকা থেকে প্রান্তটি বাতিল করে পরবর্তী প্রান্তে যান৷
-
এই অ্যালগরিদমের সময় জটিলতা হল O(E log E) বা O(E log V), যেখানে E হল প্রান্তের সংখ্যা এবং V হল শীর্ষবিন্দুর সংখ্যা৷
ইনপুট - সংলগ্ন ম্যাট্রিক্স
0 1 3 4 ∞ 5 ∞ 1 0 ∞ 7 2 ∞ ∞ 3 ∞ 0 ∞ 8 ∞ ∞ 4 7 ∞ 0 ∞ ∞ ∞ ∞ 2 8 ∞ 0 2 4 5 ∞ ∞ ∞ 2 0 3 ∞ ∞ ∞ ∞ 4 3 0
আউটপুট -
Edge: B--A And Cost: 1 Edge: E--B And Cost: 2 Edge: F--E And Cost: 2 Edge: C--A And Cost: 3 Edge: G--F And Cost: 3 Edge: D--A And Cost: 4 Total Cost: 15
অ্যালগরিদম
ক্রুস্কাল (g:গ্রাফ, t:গাছ)
ইনপুট − প্রদত্ত গ্রাফ g, এবং একটি খালি গাছ t
আউটপুট − নির্বাচিত প্রান্ত সহ ট্রি টি
Begin create set for each vertices in graph g for each set of vertex u do add u in the vertexSet[u] done sort the edge list. count := 0 while count <= V – 1 do //as tree must have V – 1 edges ed := edgeList[count] //take an edge from edge list if the starting vertex and ending vertex of ed are in same set then merge vertexSet[start] and vertexSet[end] add the ed into tree t count := count + 1 done End
উদাহরণ
#include<iostream>
#define V 7
#define INF 999
using namespace std;
//Cost matrix of the graph
int costMat[V][V] = {
{0, 1, 3, 4, INF, 5, INF},
{1, 0, INF, 7, 2, INF, INF},
{3, INF, 0, INF, 8, INF, INF},
{4, 7, INF, 0, INF, INF, INF},
{INF, 2, 8, INF, 0, 2, 4},
{5, INF, INF, INF, 2, 0, 3},
{INF, INF, INF, INF, 4, 3, 0}
};
typedef struct{
int u, v, cost;
}edge;
void swapping(edge &e1, edge &e2){
edge temp;
temp = e1;
e1 = e2;
e2 = temp;
}
class Tree{
int n;
edge edges[V-1]; //as a tree has vertex-1 edges
public:
Tree(){
n = 0;
}
void addEdge(edge e){
edges[n] = e; //add edge e into the tree
n++;
}
void printEdges(){ //print edge, cost and total cost
int tCost = 0;
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++){
cout << "Edge: " << char(edges[i].u+'A') << "--" << char(edges[i].v+'A');
cout << " And Cost: " << edges[i].cost << endl;
tCost += edges[i].cost;
}
cout << "Total Cost: " << tCost << endl;
}
};
class VSet{
int n;
int set[V];//a set can hold maximum V vertices
public:
VSet(){
n = -1;
}
void addVertex(int vert){
set[++n] = vert; //add vertex to the set
}
int deleteVertex(){
return set[n--];
}
friend int findVertex(VSet *vertSetArr, int vert);
friend void merge(VSet &set1, VSet &set2);
};
void merge(VSet &set1, VSet &set2){
//merge two vertex sets together
while(set2.n >= 0)
set1.addVertex(set2.deleteVertex());
//addToSet(vSet1, delFromSet(vSet2));
}
int findVertex(VSet *vertSetArr, int vert){
//find the vertex in different vertex sets
for(int i = 0; i<V; i++)
for(int j = 0; j<=vertSetArr[i].n; j++)
if(vert == vertSetArr[i].set[j])
return i;//node found in i-th vertex set
}
int findEdge(edge *edgeList){
//find the edges from the cost matrix of Graph and store to edgeList
int count = -1, i, j;
for(i = 0; i<V; i++)
for(j = 0; j<i; j++)
if(costMat[i][j] != INF){
count++;
//fill edge list for the position 'count'
edgeList[count].u = i; edgeList[count].v = j;
edgeList[count].cost = costMat[i][j];
}
return count+1;
}
void sortEdge(edge *edgeList, int n){
//sort the edges of graph in ascending order of cost
int flag = 1, i, j;
for(i = 0; i<(n-1) && flag; i++){//modified bubble sort is used
flag = 0;
for(j = 0; j<(n-i-1); j++)
if(edgeList[j].cost > edgeList[j+1].cost){
swapping(edgeList[j], edgeList[j+1]);
flag = 1;
}
}
}
void kruskal(Tree &tr){
int ecount, maxEdge = V*(V-1)/2; //max n(n-1)/2 edges can have in a graph
edge edgeList[maxEdge], ed;
int uloc, vloc;
VSet VSetArray[V];
ecount = findEdge(edgeList);
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
VSetArray[i].addVertex(i);//each set contains one element
sortEdge(edgeList, ecount); //ecount number of edges in the graph
int count = 0;
while(count <= V-1){
ed = edgeList[count];
uloc = findVertex(VSetArray, ed.u);
vloc = findVertex(VSetArray, ed.v);
if(uloc != vloc){ //check whether source abd dest is in same set or not
merge(VSetArray[uloc], VSetArray[vloc]);
tr.addEdge(ed);
}
count++;
}
}
int main(){
Tree tr;
kruskal(tr);
tr.printEdges();
} আউটপুট
Edge: B--A And Cost: 1 Edge: E--B And Cost: 2 Edge: F--E And Cost: 2 Edge: C--A And Cost: 3 Edge: G--F And Cost: 3 Edge: D--A And Cost: 4 Total Cost: 15


