ডেপথ ফার্স্ট সার্চ (DFS) ট্রাভার্সাল অ্যালগরিদম ব্যবহার করে আমরা একটি নির্দেশিত গ্রাফে চক্র সনাক্ত করতে পারি। কোনো নোডে কোনো স্ব-লুপ থাকলে, এটি একটি চক্র হিসেবে বিবেচিত হবে, অন্যথায়, যখন চাইল্ড নোডের অভিভাবককে সংযুক্ত করার জন্য আরেকটি প্রান্ত থাকে, তখন এটিও একটি চক্র হবে৷
সংযোগ বিচ্ছিন্ন গ্রাফের জন্য, সেখানে বিভিন্ন গাছ থাকতে পারে, আমরা তাদের একটি বন বলতে পারি। এখন আমাদের বনের সমস্ত গাছের চক্র সনাক্ত করতে হবে।
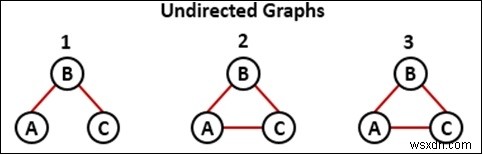
এই পদ্ধতিতে, আমরা DFS ট্র্যাভারসাল সম্পাদন করতে নোড বরাদ্দ করতে বিভিন্ন সেট ব্যবহার করব। তিনটি ভিন্ন সেট আছে, সাদা, ধূসর এবং কালো। প্রাথমিকভাবে, সমস্ত নোড সাদা সেটের ভিতরে সংরক্ষণ করা হবে। যখন একটি নতুন নোড অতিক্রম করা হয়, তখন এটি ধূসর সেটে সংরক্ষণ করা হবে এবং সাদা থেকে সরানো হবে। এবং ব্যাকট্র্যাকিং শেষ করার পরে, যখন সেই নোডের জন্য সেই কাজটি সম্পন্ন হবে, তখন এটি ধূসর থেকে কালো সেটে অদলবদল করা হবে৷
ইনপুট এবং আউটপুট
Input: The Adjacency matrix. 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 Output: The graph has cycle.
অ্যালগরিদম
dfs(curr, wSet, gSet, bSet)
ইনপুট: বর্তমান নোড, সাদা, ধূসর এবং কালো সেট।
আউটপুট: একটি চক্র থাকলে সত্য৷
৷Begin delete curr from the while set and add it to the grey set for all nodes v connected with curr in the graph, do if v is in the black set, then skip next part, and go for next iteration if v is in the grey set, then return true if dfs(v, wSet, gSet, bSet) is true, then return true done delete curr from grey set and add to black set return fasle End
হ্যা সাইকেল(গ্রাফ)
ইনপুট - দেওয়া গ্রাফ।
আউটপুট: গ্রাফটি সাইকেল করলে সত্য৷
৷Begin initially insert all nodes into the white set while white set has some elements, do for all nodes v in the graph, do if v is not in the white set, then if dfs(v, wSet, gSet, bSet), then return true done done return false End
উদাহরণ
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
#define NODE 5
using namespace std;
int graph[NODE][NODE] = {
{0, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 1, 0, 0}
};
bool dfs(int curr, set<int>&wSet, set<int>&gSet, set<int>&bSet) {
//moving curr to white set to grey set.
wSet.erase(wSet.find(curr));
gSet.insert(curr);
for(int v = 0; v < NODE; v++) {
if(graph[curr][v] != 0) { //for all neighbour vertices
if(bSet.find(v) != bSet.end())
continue; //if the vertices are in the black set
if(gSet.find(v) != gSet.end())
return true; //it is a cycle
if(dfs(v, wSet, gSet, bSet))
return true; //cycle found
}
}
//moving v to grey set to black set.
gSet.erase(gSet.find(curr));
bSet.insert(curr);
return false;
}
bool hasCycle() {
set<int> wSet, gSet, bSet; //three set as white, grey and black
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++)
wSet.insert(i); //initially add all node into the white set
while(wSet.size() > 0) {
for(int current = 0; current < NODE; current++) {
if(wSet.find(current) != wSet.end())
if(dfs(current, wSet, gSet, bSet))
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
int main() {
bool res;
res = hasCycle();
if(res)
cout << "The graph has cycle." << endl;
else
cout << "The graph has no cycle." << endl;
} আউটপুট
The graph has cycle.


