একটি অনির্দেশিত গ্রাফকে একটি দ্বিসংযুক্ত গ্রাফ বলা হয়, যদি দুটি শীর্ষবিন্দুর মধ্যে দুটি শীর্ষবিন্দু-বিচ্ছিন্ন পথ থাকে। অন্য কথায়, আমরা বলতে পারি যে কোনো দুটি শীর্ষবিন্দুর মধ্যে একটি চক্র আছে।
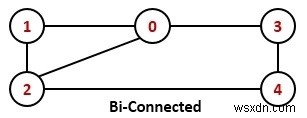
আমরা বলতে পারি যে একটি গ্রাফ G একটি দ্বি-সংযুক্ত গ্রাফ যদি এটি সংযুক্ত থাকে এবং গ্রাফটিতে কোন উচ্চারণ বিন্দু বা কাটা শীর্ষবিন্দু উপস্থিত থাকে না।
এই সমস্যা সমাধানের জন্য, আমরা DFS ট্রাভার্সাল ব্যবহার করব। DFS ব্যবহার করে, আমরা খুঁজে বের করার চেষ্টা করব যে কোনো আর্টিকুলেশন পয়েন্ট আছে কি না। আমরা এটিও পরীক্ষা করি যে সমস্ত শীর্ষগুলি DFS দ্বারা পরিদর্শন করা হয়েছে কিনা, যদি না হয় তবে আমরা বলতে পারি যে গ্রাফটি সংযুক্ত নয়৷
ইনপুট এবং আউটপুট
Input: The adjacency matrix of the graph. 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 Output: The Graph is a biconnected graph.
অ্যালগরিদম
আর্টিকুলেশন (শুরু, পরিদর্শন করা, ডিস্ক, কম, অভিভাবক)
ইনপুট: প্রারম্ভিক শীর্ষবিন্দু, একটি নোড পরিদর্শন করা হলে চিহ্নিত করার জন্য পরিদর্শন করা অ্যারে, ডিস্কটি শীর্ষবিন্দুর আবিষ্কারের সময় ধরে রাখবে এবং নিম্নে সাবট্রি সম্পর্কে তথ্য থাকবে। অভিভাবক বর্তমান শীর্ষবিন্দুর অভিভাবককে ধরে রাখবে৷
৷আউটপুট - কোনো উচ্চারণ বিন্দু পাওয়া গেলে সত্য।
Begin time := 0 //the value of time will not be initialized for next function calls dfsChild := 0 mark start as visited set disc[start] := time+1 and low[start] := time + 1 time := time + 1 for all vertex v in the graph G, do if there is an edge between (start, v), then if v is visited, then increase dfsChild parent[v] := start if isArticulation(v, visited, disc, low, parent) is true, then return ture low[start] := minimum of low[start] and low[v] if parent[start] is φ AND dfsChild > 1, then return true if parent[start] is φ AND low[v] >= disc[start], then return true else if v is not the parent of start, then low[start] := minimum of low[start] and disc[v] done return false End
দ্বিসংযুক্ত(গ্রাফ)
ইনপুট: প্রদত্ত গ্রাফ।
আউটপুট - গ্রাফটি দ্বি-সংযুক্ত হলে সত্য।
Begin initially set all vertices are unvisited and parent of each vertices are φ if isArticulation(0, visited, disc, low, parent) = true, then return false for each node i of the graph, do if i is not visited, then return false done return true End
উদাহরণ
#include<iostream>
#define NODE 5
using namespace std;
int graph[NODE][NODE] = {
{0, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 0}
};
int min(int a, int b) {
return (a<b)?a:b;
}
bool isArticulation(int start, bool visited[], int disc[], int low[], int parent[]) {
static int time = 0;
int dfsChild = 0;
visited[start] = true; //make the first vertex is visited
disc[start] = low[start] = ++time; //initialize discovery time and the low time
for(int v = 0; v<NODE; v++) {
if(graph[start][v]) { //for all vertex v, which is connected with start
if(!visited[v]) {
dfsChild++;
parent[v] = start; //make start node as parent
if(isArticulation(v, visited, disc, low, parent))
return true;
low[start] = min(low[start], low[v]); //when subtree from v is connected to one of parent of start node
if(parent[start] == -1 && dfsChild > 1) { //when u have 2 or more children
return true;
}
if(parent[start] != -1 && low[v]>= disc[start])
return true;
} else if(v != parent[start]) //update low of start for previous call
low[start] = min(low[start], disc[v]);
}
}
return false;
}
bool isBiConnected() {
bool *vis = new bool[NODE];
int *disc = new int[NODE];
int *low = new int[NODE];
int *parent = new int[NODE];
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++) {
vis[i] = false; //no node is visited
parent[i] = -1; //initially there is no parent for any node
}
if(isArticulation(0, vis, disc, low, parent)) //when no articulation point is found
return false;
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++)
if(!vis[i]) //if any node is unvisited, the graph is not connected
return false;
return true;
}
int main() {
if(isBiConnected())
cout << "The Graph is a biconnected graph.";
else
cout << "The Graph is not a biconnected graph.";
} আউটপুট
The Graph is a biconnected graph.


