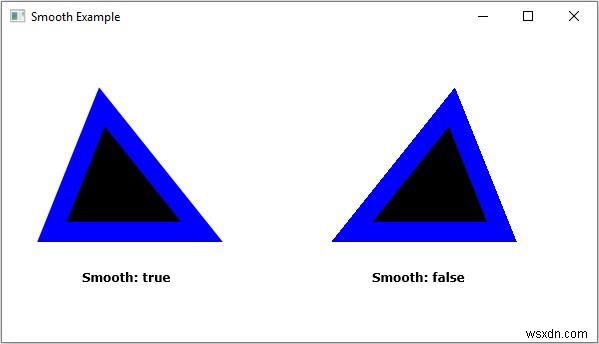
মসৃণ বৈশিষ্ট্যটি নির্দিষ্ট করে যে অ্যান্টিলিয়াসিং ইঙ্গিতগুলি ব্যবহার করা হয়েছে কি না৷ আপনি setSmooth() ব্যবহার করে এই সম্পত্তিতে মান সেট করতে পারেন javafx.scene.shape.shape এর পদ্ধতি ক্লাস।
এই পদ্ধতিটি একটি বুলিয়ান মান গ্রহণ করে এবং আপনি যদি সত্য পাস করেন তবে আকৃতির প্রান্তগুলি মসৃণ করা হবে৷
উদাহরণ
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.shape.Polygon;
import javafx.scene.shape.StrokeLineJoin;
import javafx.scene.text.Font;
import javafx.scene.text.FontPosture;
import javafx.scene.text.FontWeight;
import javafx.scene.text.Text;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class SmoothExample extends Application {
public void start(Stage stage) {
Font font = Font.font("verdana", FontWeight.BOLD, FontPosture.REGULAR, 12);
Text label2 = new Text("Smooth: true");
label2.setFont(font);
label2.setX(80.0);
label2.setY(250.0);
Polygon shape1 = new Polygon(100.0, 75.0, 50.0, 200.0, 200.0, 200.0);
shape1.setStroke(Color.BLUE);
shape1.setStrokeWidth(20);
shape1.setStrokeLineJoin(StrokeLineJoin.MITER);
shape1.setSmooth(true);
Text label3 = new Text("Smooth: false");
label3.setFont(font);
label3.setX(370.0);
label3.setY(250.0);
Polygon shape2 = new Polygon(450.0, 75.0, 350.0, 200.0, 500.0, 200.0);
shape2.setStroke(Color.BLUE);
shape2.setStrokeWidth(20.0);
shape2.setStrokeLineJoin(StrokeLineJoin.MITER);
shape2.setSmooth(false);
//Creating a Group object
Group root = new Group(label2, label3, shape1, shape2);
//Creating a scene object
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 595, 310);
//Setting title to the Stage
stage.setTitle("Smooth Example");
//Adding scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
} আউটপুট