ধরুন, একটি ওজনযুক্ত, অনির্দেশিত গ্রাফ রয়েছে যার n শীর্ষবিন্দু এবং m প্রান্ত রয়েছে। গ্রাফের স্কোরকে গ্রাফের সমস্ত প্রান্তের ওজনের যোগ হিসাবে সংজ্ঞায়িত করা হয়। প্রান্তের ওজন ঋণাত্মক হতে পারে, এবং সেগুলি সরানো হলে গ্রাফের স্কোর বৃদ্ধি পায়। আমাদের যা করতে হবে, গ্রাফ সংযুক্ত রেখে গ্রাফ থেকে প্রান্তগুলি সরিয়ে গ্রাফের স্কোর ন্যূনতম করতে হবে। আমাদের খুঁজে বের করতে হবে সর্বোচ্চ কত স্কোর কমানো যায়।
গ্রাফটি একটি অ্যারে 'এজ'-এ দেওয়া হয়েছে, যেখানে প্রতিটি উপাদানের আকার {weight, {vertex1, vertex2}}৷
সুতরাং, যদি ইনপুট হয় n =5, m =6, প্রান্ত ={{2, {1, 2}}, {2, {1, 3}}, {1, {2, 3}}, {3 , {2, 4}}, {2, {2, 5}}, {1, {3, 5}}}, তাহলে আউটপুট হবে 4।
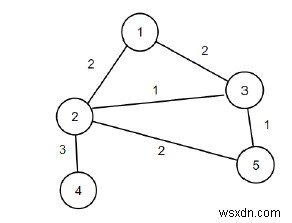
যদি আমরা গ্রাফ থেকে প্রান্ত (1, 2) এবং (2, 5) মুছে ফেলি, তাহলে স্কোরের মোট হ্রাস হবে 4 এবং গ্রাফটি সংযুক্ত থাকবে৷
এটি সমাধান করতে, আমরা এই পদক্ষেপগুলি অনুসরণ করব−
cnum := 0
Define an array par of size: 100.
Define an array dim of size: 100.
Define a function make(), this will take v,
par[v] := v
dim[v] := 1
Define a function find(), this will take v,
if par[v] is same as v, then:
return v
return par[v] = find(par[v])
Define a function unify(), this will take a, b,
a := find(a)
b := find(b)
if a is not equal to b, then:
(decrease cnum by 1)
if dim[a] > dim[b], then:
swap values of (a, b)
par[a] := b
dim[b] := dim[b] + dim[a]
cnum := n
sort the array edges based on edge weights
for initialize i := 1, when i <= n, update (increase i by 1), do:
make(i)
res := 0
for each edge in edges, do:
a := first vertex of edge
b := second vertex of edge
weight := weight of edge
if find(a) is same as find(b), then:
if weight >= 0, then:
res := res + 1 * weight
Ignore following part, skip to the next iteration
if cnum is same as 1, then:
if weight >= 0, then:
res := res + 1 * weight
Otherwise
unify(a, b)
return res উদাহরণ
আরো ভালোভাবে বোঝার জন্য আসুন নিচের বাস্তবায়ন দেখি -
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int cnum = 0;
int par[100];
int dim[100];
void make(int v){
par[v] = v;
dim[v] = 1;
}
int find(int v){
if(par[v] == v)
return v;
return par[v] = find(par[v]);
}
void unify(int a, int b){
a = find(a); b = find(b);
if(a != b){
cnum--; if(dim[a] > dim[b]){
swap(a, b);
}
par[a] = b; dim[b] += dim[a];
}
}
int solve(int n, int m, vector <pair <int, pair<int,int>>> edges){
cnum = n;
sort(edges.begin(), edges.end());
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
make(i);
int res = 0;
for(auto &edge : edges){
int a = edge.second.first;
int b = edge.second.second;
int weight = edge.first;
if(find(a) == find(b)) {
if(weight >= 0)
res += 1 * weight;
continue;
}
if(cnum == 1){
if(weight >= 0)
res += 1 * weight;
} else{
unify(a, b);
}
}
return res;
}
int main() {
int n = 5, m = 6;
vector <pair<int, pair<int,int>>> edges = {{2, {1, 2}}, {2, {1, 3}}, {1, {2, 3}}, {3, {2, 4}}, {2, {2, 5}}, {1, {3, 5}}};
cout<< solve(n, m, edges);
return 0;
} ইনপুট
5, 6, {{2, {1, 2}}, {2, {1, 3}}, {1, {2, 3}}, {3, {2, 4}}, {2, {2, 5}}, {1, {3, 5}}}
আউটপুট
4


