ধরুন, আমাদের একটি গ্রাফ দেওয়া হয়েছে যার n শীর্ষবিন্দু রয়েছে। শীর্ষবিন্দুগুলি 1 থেকে n পর্যন্ত সংখ্যাযুক্ত, এবং তারা অ্যারে 'এজ'-এ দেওয়া প্রান্তগুলি দ্বারা সংযুক্ত। প্রতিটি শীর্ষে 1 থেকে n পর্যন্ত একটি সংখ্যার মধ্যে একটি 'x' মান থাকে যা অ্যারে 'মান'-এ দেওয়া হয়। এখন, আমাদের গ্রাফ থেকে সুপার শীর্ষবিন্দুগুলি খুঁজে বের করতে হবে। একটি শীর্ষবিন্দু i একটি 'সুপার ভার্টেক্স' বলা হয় যখনই শীর্ষবিন্দু 1 থেকে i পর্যন্ত সংক্ষিপ্ততম পথটিতে i-তম শীর্ষবিন্দুর মতো একই 'x' মান সহ একটি শীর্ষবিন্দু থাকে না। আমরা এই মানদণ্ডকে সন্তুষ্ট করে এমন সমস্ত শীর্ষবিন্দু মুদ্রণ করি৷
৷
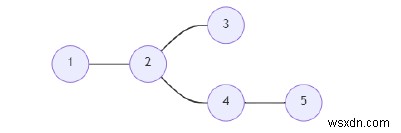
সুতরাং, যদি ইনপুট n =5 এর মত হয়, মান ={1, 2, 2, 1, 3}, প্রান্ত ={{1, 2}, {2, 3}, {2, 3}, {2, 4 }, {4, 5}}, তাহলে আউটপুট হবে 1 3 4 5।
শীর্ষবিন্দু 2 ব্যতীত প্রতিটি শীর্ষবিন্দু মানদণ্ডকে সন্তুষ্ট করে। সুতরাং, শীর্ষবিন্দু 2 বাদ দেওয়া হয়েছে।
পদক্ষেপ
এটি সমাধান করতে, আমরা এই পদক্ষেপগুলি অনুসরণ করব -
Define arrays vertexVal, frq, and chk of size: 100005. Define an array vcti of size 200005. Define a function dfs(), this will take j, k, if frq[vertexVal[j]] is same as 0, then: chk[j] := 1 (increase frq[vertexVal[j]] by 1) for each value a in vcti[j], do: if a is not equal to k, then: dfs(a, j) (decrease frq[vertexVal[j]] by 1) for initialize i := 0, when i < n, update (increase i by 1), do: vertexVal[i] := values[i] for initialize i := 0, when i < n, update (increase i by 1), do: a := first value of edges[i] b := second value of edges[i] insert b at the end of vcti[a] insert a at the end of vcti[b] dfs(1, 0) for initialize i := 1, when i <= n, update (increase i by 1), do: if chk[i] is non-zero, then: print(i)
উদাহরণ
আরো ভালোভাবে বোঝার জন্য আসুন নিচের বাস্তবায়ন দেখি -
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n;
int vertexVal[100005], frq[100005], chk[100005];
vector<int> vcti[200005];
void dfs(int j, int k){
if (frq[vertexVal[j]] == 0)
chk[j] = 1;
frq[vertexVal[j]]++;
for (auto a : vcti[j]) {
if (a != k)
dfs(a, j);
}
frq[vertexVal[j]]--;
}
void solve(int values[], vector<pair<int, int>> edges){
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
vertexVal[i] = values[i];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int a, b;
a = edges[i].first;
b = edges[i].second;
vcti[a].push_back(b);
vcti[b].push_back(a);
}
dfs(1, 0);
for (int i = 1;i <= n; i++){
if (chk[i]) cout<< i <<endl;
}
}
int main() {
n = 5;
int values[] = {1, 2, 2, 1, 3}; vector<pair<int, int>> edges = {{1, 2}, {2, 3}, {2, 3}, {2, 4}, {4, 5}};
solve(values, edges);
return 0;
} ইনপুট
5, {1, 2, 2, 1, 3}, {{1, 2}, {2, 3}, {2, 3}, {2, 4}, {4, 5}} আউটপুট
1 3 4 5


