এখানে একটি সংযুক্ত গ্রাফ G(V, E) রয়েছে এবং প্রতিটি প্রান্তের ওজন বা খরচ দেওয়া হয়েছে৷ Prim's Algorithm G গ্রাফ থেকে ন্যূনতম স্প্যানিং ট্রি খুঁজে পাবে।
এটি একটি ক্রমবর্ধমান গাছ পদ্ধতি। এই অ্যালগরিদম গাছ শুরু করার জন্য একটি বীজ মান প্রয়োজন. বীজ শীর্ষবিন্দু পুরো গাছ গঠনের জন্য বড় হয়।
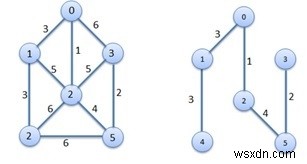
দুটি সেট ব্যবহার করে সমস্যার সমাধান করা হবে। একটি সেট ইতিমধ্যেই নির্বাচিত নোডগুলিকে ধারণ করে, এবং অন্য সেটটি এখনও বিবেচনা করা হয়নি এমন আইটেমগুলিকে ধারণ করে৷ বীজ শীর্ষবিন্দু থেকে, এটি ন্যূনতম প্রান্ত খরচের উপর ভিত্তি করে সংলগ্ন শীর্ষবিন্দুগুলি নেয়, এইভাবে এটি একে একে নোড নিয়ে গাছ বৃদ্ধি করে।
এই সমস্যার সময় জটিলতা হল O(V^2)। এখানে V হল শীর্ষবিন্দুর সংখ্যা।
ইনপুট এবং আউটপুট
Input: The adjacency list:Output: (0)---(1|1) (0)---(2|3) (0)---(3|4) (1)---(0|1) (1)---(4|2) (2)---(0|3) (3)---(0|4) (4)---(1|2) (4)---(5|2) (5)---(4|2) (5)---(6|3) (6)---(5|3)
অ্যালগরিদম
prims(g: Graph, t: tree, start)
ইনপুট - গ্রাফ g, একটি ফাঁকা গাছ এবং 'start'
নামের বীজের শীর্ষবিন্দুআউটপুট - প্রান্ত যোগ করার পর গাছ।
Begin define two sets as usedVert, unusedVert usedVert[0] := start and unusedVert[0] := φ for all vertices except start do usedVert[i] := φ unusedVert[i] := i //add all vertices in unused list done while number of vertices in usedVert ≠ V do //V is number of total nodes min := ∞ for all vertices of usedVert array do for all vertices of the graph do if min > cost[i,j] AND i ≠ j then min := cost[i,j] ed := edge between i and j, and cost of ed := min done done unusedVert[destination of ed] := φ add edge ed into the tree t add source of ed into usedVert done End
উদাহরণ
#include<iostream>
#define V 7
#define INF 999
using namespace std;
//Cost matrix of the graph
int costMat[V][V] = {
{0, 1, 3, 4, INF, 5, INF},
{1, 0, INF, 7, 2, INF, INF},
{3, INF, 0, INF, 8, INF, INF},
{4, 7, INF, 0, INF, INF, INF},
{INF, 2, 8, INF, 0, 2, 4},
{5, INF, INF, INF, 2, 0, 3},
{INF, INF, INF, INF, 4, 3, 0}
};
typedef struct {
int u, v, cost;
}edge;
class Tree {
int n;
edge edges[V-1]; //as a tree has vertex-1 edges
public:
Tree() {
n = 0;
}
void addEdge(edge e) {
edges[n] = e; //add edge e into the tree
n++;
}
void printEdges() { //print edge, cost and total cost
int tCost = 0;
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++) {
cout << "Edge: " << char(edges[i].u+'A') << "--" << char(edges[i].v+'A');
cout << " And Cost: " << edges[i].cost << endl;
tCost += edges[i].cost;
}
cout << "Total Cost: " << tCost << endl;
}
friend void prims(Tree &tre, int start);
};
void prims(Tree &tr, int start) {
int usedVert[V], unusedVert[V];
int i, j, min, p;
edge ed;
//initialize
usedVert[0] = start; p = 1;
unusedVert[0] = -1; //-1 indicates the place is empty
for(i = 1; i<V; i++) {
usedVert[i] = -1; //all places except first is empty
unusedVert[i] = i; //fill with vertices
}
tr.n = 0;
//get edges and add to tree
while(p != V) { //p is number of vertices in usedVert array
min = INF;
for(i = 0; i<p; i++) {
for(j = 0; j<V; j++) {
if(unusedVert[j] != -1) {
if(min > costMat[i][j] && costMat[i][j] != 0) {
//find the edge with minimum cost
//such that u is considered and v is not considered yet
min = costMat[i][j];
ed.u = i; ed.v = j; ed.cost = min;
}
}
}
}
unusedVert[ed.v] = -1; //delete v from unusedVertex
tr.addEdge(ed);
usedVert[p] = ed.u; p++; //add u to usedVertex
}
}
main() {
Tree tr;
prims(tr, 0); //starting node 0
tr.printEdges();
} আউটপুট
(0)---(1|1) (0)---(2|3) (0)---(3|4) (1)---(0|1) (1)---(4|2) (2)---(0|3) (3)---(0|4) (4)---(1|2) (4)---(5|2) (5)---(4|2) (5)---(6|3) (6)---(5|3)


