বাইনারি ট্রি দেওয়া হলে, ফাংশনটি নোডগুলিতে সংরক্ষিত কীগুলির বাইনারি মান তৈরি করবে এবং তারপর সেই বাইনারি সমতুল্য সেট বিটের সংখ্যা(1) প্রদান করবে।
উদাহরণ
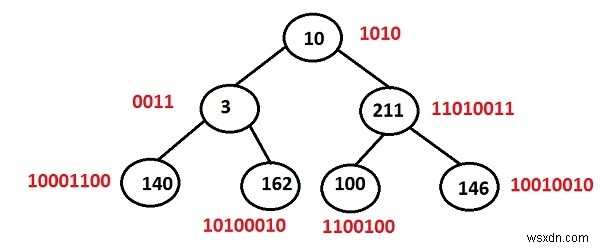
বাইনারি গাছের চাবি আছে:10 3 211 140 162 100 এবং 146
| কী | বাইনারি সমতুল্য | বিট সেট করুন(আউটপুট) |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 1010 | 2 |
| 3 | 0011 | 2 |
| 211 | 11010011 | 5 |
| 140 | 10001100 | 3 |
| 162 | 10100010 | 3 |
| 100 | 1100100 | 3 |
| 146 | 10010010 | 3 |
এখানে আমরা ফাংশনটি ব্যবহার করছি __builtin_popcount
ফাংশনের প্রোটোটাইপটি নিম্নরূপ -
int __builtin_popcount(unsigned int)
এটি একটি পূর্ণসংখ্যাতে সেট বিটের সংখ্যা প্রদান করে অর্থাৎ পূর্ণসংখ্যার বাইনারি উপস্থাপনায় সংখ্যার সংখ্যা।
অ্যালগরিদম
START Step 1 -> create a structure of a node as struct Node struct node *left, *right int data End Step 2 -> function to create a node node* newnode(int data) node->data = data node->left = node->right = NULL; return (node) Step 3 -> Create function for generating bits of a node data void bits(Node* root) IF root = NULL return print __builtin_popcount(root->data) bits(root->left) bits(root->right) step 4 -> In main() create tree using Node* root = newnode(10) root->left = newnode(3) call bits(root) STOP
উদাহরণ
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// structure of a node
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
//function to create a new node
Node* newnode(int data) {
Node* node = new Node;
node->data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
//function for finding out the node
void bits(Node* root){
if (root == NULL)
return;
//__builtin_popcount counts the number of set bit of a current node
cout << "bits in node " << root->data << " = " <<__builtin_popcount(root->data)<< "\n";
bits(root->left);
bits(root->right);
}
int main(){
Node* root = newnode(10);
root->left = newnode(3);
root->left->left = newnode(140);
root->left->right = newnode(162);
root->right = newnode(211);
root->right->left = newnode(100);
root->right->right = newnode(146);
bits(root);
return 0;
} আউটপুট
যদি আমরা উপরের প্রোগ্রামটি চালাই তাহলে এটি নিম্নলিখিত আউটপুট তৈরি করবে
bits in node 10 = 2 bits in node 3 = 2 bits in node 140 = 3 bits in node 162 = 3 bits in node 211 = 5 bits in node 100 = 3 bits in node 146 = 3


