ধারণা
নিবন্ধটি একটি গাছে দুটি নোডের এলসিএ খুঁজে পাওয়ার সমস্যাটিকে RMQ সমস্যায় হ্রাস করে সমাধান করার একটি পদ্ধতি ব্যাখ্যা করে৷
উদাহরণ
নিম্নতম সাধারণ পূর্বপুরুষ (LCA) একটি শিকড়যুক্ত গাছে দুটি নোড a এবং b এর T কে মূল থেকে সবচেয়ে দূরে অবস্থিত নোড হিসাবে সংজ্ঞায়িত করা হয় যার বংশধর হিসাবে a এবং b উভয়ই রয়েছে।
উদাহরণস্বরূপ, নীচের চিত্র অনুসারে, নোড D এর LCA এবং নোড I হল নোড B৷
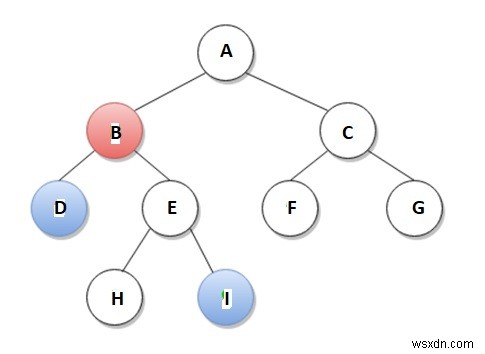
আমরা LCA সমস্যা সমাধানের জন্য অনেক পন্থা প্রয়োগ করতে পারি। এই পন্থাগুলি তাদের সময় এবং স্থান জটিলতার ক্ষেত্রে আলাদা।
রেঞ্জ ন্যূনতম কোয়েরি (RMQ) দুটি নির্দিষ্ট সূচকের মধ্যে ন্যূনতম মান সহ একটি উপাদানের অবস্থান সনাক্ত করতে অ্যারেতে প্রয়োগ করা হয়। আমরা RMQ সমাধানের জন্য বিভিন্ন পন্থা প্রয়োগ করতে পারি। এই নিবন্ধ অনুসারে, সেগমেন্ট ট্রি ভিত্তিক পদ্ধতির ব্যাখ্যা করা হয়েছে। সেগমেন্ট ট্রির ক্ষেত্রে, প্রিপ্রসেসিং টাইম হল O(n) এবং রেঞ্জ ন্যূনতম কোয়েরির জন্য সময় হল O(Logn)। এখানে, সেগমেন্ট ট্রি সংরক্ষণ করার জন্য অতিরিক্ত স্থানের প্রয়োজন O(n)।
এলসিএ থেকে RMQ থেকে হ্রাস
আমরা একটি অয়লার ট্যুর (পেন্সিল উত্তোলন ছাড়াই ভিজিট) দ্বারা গাছের মূল থেকে শুরু করে পরিদর্শন করার জন্য এই ধারণাটি ব্যাখ্যা করি, যা একটি ডিএফএস(ডেপথ ফার্স্ট সার্চ)-প্রি-অর্ডার ট্রাভার্সাল বৈশিষ্ট্য সহ ট্রাভার্সাল।
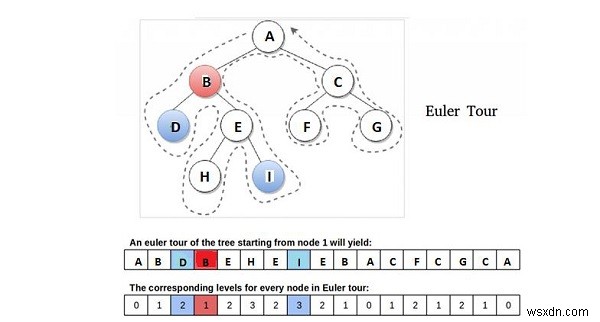
পর্যবেক্ষণ − উপরের চিত্র অনুসারে, নোড D এবং I-এর LCA হল নোড B, যা নির্দেশ করে যে T-এর DFS-এর সময় D এবং I-এর ভিজিটগুলির মধ্যে যাদের সম্মুখীন হয়েছে তাদের মধ্যে মূলের সবচেয়ে কাছের নোড। তাই আমরা এই পর্যবেক্ষণ বলতে পারি। হ্রাসের চাবিকাঠি। আবার আমরা বলতে পারি যে আমাদের নোডটি সর্বনিম্ন স্তরের নোড এবং টি-এর অয়লার সফরে পরপর (যেকোনো) a এবং b এর মধ্যে ঘটে যাওয়া সমস্ত নোডের মধ্যে সেই স্তরের একমাত্র নোড।
বাস্তবায়নের জন্য আমাদের তিনটি অ্যারে প্রয়োজন -
-
T
এর অয়লার সফরের ক্রমানুসারে পরিদর্শন করা নোড -
T
এর অয়লার সফরে প্রতিটি নোড লেভেল পরিদর্শন করা হয়েছে -
T-এর অয়লার সফরে নোডের প্রথম ঘটনা সূচক (যেহেতু যেকোনো ঘটনাই ভালো হবে, আসুন প্রথমটিকে ট্র্যাক করি)
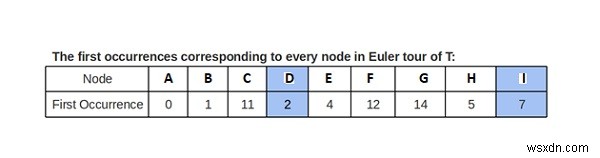
পদ্ধতি
-
গাছে অয়লার ট্যুর করুন এবং ইউলার, লেভেল এবং প্রথম ঘটনা অ্যারে পূরণ করুন।
-
প্রথম সংঘটন অ্যারে প্রয়োগ করে, ন্যূনতম মানের জন্য RMQ অ্যালগরিদমে খাওয়ানো যে স্তর অ্যারেতে পরিসরের কোণগুলি হবে দুটি নোডের সাথে সম্পর্কিত সূচকগুলি পান৷
-
যে সময়ে অ্যালগরিদম পরিসরে ন্যূনতম স্তরের সূচক ফেরত দেয়, তখন আমরা অয়লার ট্যুর অ্যারে ব্যবহার করে এলসিএ নির্ধারণ করতে এটি প্রয়োগ করি৷
উদাহরণ
/* This C++ Program is implemented to find LCA of u and v by reducing the problem to RMQ */
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define V 9 // indicates number of nodes in input tree
int euler1[2*V - 1]; // indicates for Euler tour sequence
int level1[2*V - 1]; // indicates level of nodes in tour sequence
int firstOccurrence1[V+1]; // indicates first occurrences of nodes in tour
int ind; // indicates variable to fill-in euler and level arrays
//This is a Binary Tree node
struct Node1{
int key;
struct Node1 *left, *right;
};
// Utility function creates a new binary tree node with given key
Node1 * newNode1(int k){
Node1 *temp = new Node1;
temp->key = k;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// indicates log base 2 of x
int Log2(int x){
int ans = 0 ;
while (x>>=1) ans++;
return ans ;
}
/* A recursive function is used to get the minimum value in a given range of array indexes. The following are parameters for this function.
st --> indicates pointer to segment tree
index --> indicates index of current node in the segment tree.
Initially 0 is passed as root is always at index 0
ss & se --> indicate starting and ending indexes of the segment
represented by current node, i.e., st[index]
qs & qe --> indicate starting and ending indexes of query range
*/
int RMQUtil(int index1, int ss1, int se1, int qs1, int qe1, int *st1){
// It has been seen that if segment of this node is a part of given range, then return the min of the segment
if (qs1 <= ss1 && qe1 >= se1)
return st1[index1];
//It has been seen that if segment of this node is outside the given range
else if (se1 < qs1 || ss1 > qe1)
return -1;
// It has been seen that if a part of this segment overlaps with the given range
int mid = (ss1 + se1)/2;
int q1 = RMQUtil(2*index1+1, ss1, mid, qs1, qe1, st1);
int q2 = RMQUtil(2*index1+2, mid+1, se1, qs1, qe1, st1);
if (q1==-1) return q2;
else if (q2==-1) return q1;
return (level1[q1] < level1[q2]) ? q1 : q2;
}
// Return minimum of elements in range from index qs (query start) to
// qe (query end). It mainly uses RMQUtil()
int RMQ(int *st1, int n, int qs1, int qe1){
// Check for erroneous input values
if (qs1 < 0 || qe1 > n-1 || qs1 > qe1){
printf("Invalid Input");
return -1;
}
return RMQUtil(0, 0, n-1, qs1, qe1, st1);
}
// Now a recursive function that constructs Segment Tree for
array[ss1..se1]. // si1 is index of current node in segment tree st
void constructSTUtil(int si1, int ss1, int se1, int arr1[], int *st1){
// When there will be only one element in array, store it in current node of
// segment tree and return
if (ss1 == se1)st1[si1] = ss1;
else{
// It has been seen that if there are more than one
elements, then recur for left and right subtrees and store the
minimum of two values in this node
int mid1 = (ss1 + se1)/2;
constructSTUtil(si1*2+1, ss1, mid1, arr1, st1);
constructSTUtil(si1*2+2, mid1+1, se1, arr1, st1);
if (arr1[st1[2*si1+1]] < arr1[st1[2*si1+2]])
st1[si1] = st1[2*si1+1];
else
st1[si1] = st1[2*si1+2];
}
}
/* Now this function is used to construct segment tree from given
array. This function allocates memory for segment tree and calls
constructSTUtil() to fill the allocated memory */
int *constructST(int arr1[], int n){
// Allocating memory for segment tree
//Indicates height of segment tree
int x = Log2(n)+1;
// Indicates maximum size of segment tree
int max_size = 2*(1<<x) - 1; // 2*pow(2,x) -1
int *st1 = new int[max_size];
// Indicates filling the allocated memory st1
constructSTUtil(0, 0, n-1, arr1, st1);
// Returning the constructed segment tree
return st1;
}
// Indicates recursive version of the Euler tour of T
void eulerTour(Node1 *root, int l){
/* if the passed node exists */
if (root){
euler1[ind] = root->key; // inserting in euler array
level1[ind] = l; // inserting l in level array
ind++; // indicates increment index
/* It has been seen that if unvisited, mark first occurrence*/
if (firstOccurrence1[root->key] == -1)
firstOccurrence1[root->key] = ind-1;
/* touring left subtree if exists, and remark euler
and level arrays for parent on return */
if (root->left){
eulerTour(root->left, l+1);
euler1[ind]=root->key;
level1[ind] = l;
ind++;
}
/* touring right subtree if exists, and remark euler
and level arrays for parent on return */
if (root->right) {
eulerTour(root->right, l+1);
euler1[ind]=root->key;
level1[ind] = l;
ind++;
}
}
}
// Returning LCA of nodes n1, n2 (assuming they are
// present in the tree)
int findLCA(Node1 *root, int u1, int v1){
/* Marking all nodes unvisited. Note that the size of
firstOccurrence is 1 as node values which vary from
1 to 9 are used as indexes */
memset(firstOccurrence1, -1, sizeof(int)*(V+1));
/* To start filling euler and level arrays from index 0 */
ind = 0;
/* Starting Euler tour with root node on level 0 */
eulerTour(root, 0);
/* constructing segment tree on level array */
int *st1 = constructST(level1, 2*V-1);
/*It has been seen that if v before u in Euler tour. For RMQ to
work, first parameter 'u1' must be smaller than second 'v1' */
if (firstOccurrence1[u1]>firstOccurrence1[v1])
std::swap(u1, v1);
// Indicates starting and ending indexes of query range
int qs1 = firstOccurrence1[u1];
int qe1 = firstOccurrence1[v1];
// Indicates query for index of LCA in tour
int index1 = RMQ(st1, 2*V-1, qs1, qe1);
/* returning LCA node */
return euler1[index1];
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main(){
// Let us create the Binary Tree as shown in the diagram.
Node1 * root = newNode1(1);
root->left = newNode1(2);
root->right = newNode1(3);
root->left->left = newNode1(4);
root->left->right = newNode1(5);
root->right->left = newNode1(6);
root->right->right = newNode1(7);
root->left->right->left = newNode1(8);
root->left->right->right = newNode1(9);
int u1 = 4, v1 = 9;
printf("The LCA of node %d and node %d is node %d.\n",
u1, v1, findLCA(root, u1, v1));
return 0;
} আউটপুট
The LCA of node 4 and node 9 is node 2.


