বাইনারি ট্রি দেওয়া হলে প্রোগ্রামটিকে মূল থেকে একটি পাতা পর্যন্ত একাধিক পথ খুঁজে বের করতে হবে যার মানে সমস্ত পথ প্রিন্ট করা উচিত কিন্তু চ্যালেঞ্জ হল পুনরাবৃত্তি ব্যবহার না করেই।
আমরা পুনরাবৃত্তভাবে গাছটি অতিক্রম করব কারণ সীমাবদ্ধতা হল এটি পুনরাবৃত্তি ছাড়াই করা। তাই এটি অর্জনের জন্য আমরা একটি STL মানচিত্র ব্যবহার করতে পারি যা রুট উপাদান সংরক্ষণ করবে এবং যখনই লিফ নোডটি লেভেল অর্ডার ট্রাভার্সালের মাধ্যমে চিহ্নিত করা হবে এটি রুট থেকে পাতার পথ প্রিন্ট করবে কারণ সেখানে একটি মানচিত্র পয়েন্টার রয়েছে যা একটি রুট নোডকে নির্দেশ করছে।
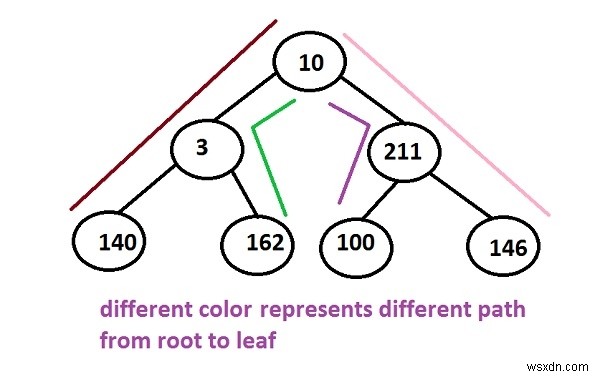
উপরের গাছে, মূল থেকে পাতায় পৌঁছানোর জন্য একাধিক পথ তৈরি করা যেতে পারে -
10 -> 3 -> 140 10 -> 3 -> 162 10 -> 211 -> 100 10 -> 211 -> 146
তাই, প্রোগ্রামটিকে প্রদত্ত বাইনারি ট্রির আউটপুট হিসাবে প্রদত্ত সমস্ত পথ প্রিন্ট করতে হবে৷
অ্যালগরিদম
START Step 1 -> create a structure of a node as struct Node struct node *left, *right int data End Step 2 -> function to create a node node* newnode(int data) node->data = data node->left = node->right = NULL; return (node) Step 3 -> create function to calculate the path void calculatePath(Node* curr, map<Node*, Node*> first) create STL stack<Node*> stk Loop While (curr) stk.push(curr) curr = first[curr] End Loop While !stk.empty() curr = stk.top() stk.pop() print curr->data End Step 4 -> create function to find the leaf nodes void leaf(Node* root) IF root = NULL Return End Create STL stack<Node*> stc stc.push(root) Create STL map<Node*, Node*> prnt prnt[root] = NULL Loop while !stc.empty() Node* curr = stc.top() stc.pop() IF!(curr->left) && !(curr->right) calculatePath(curr, prnt) End IF curr->right prnt[curr->right] = curr stc.push(curr->right) End IF curr->left prnt[curr->left] = curr stc.push(curr->left) End End STOP
উদাহরণ
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//structure of a node
struct Node{
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
//function to create a new node
Node* newNode(int data){
Node* node = new Node;
node->data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
//this function will calculate the path
void calculatePath(Node* curr, map<Node*, Node*> first){
stack<Node*> stk;
while (curr){
stk.push(curr);
curr = first[curr];
}
while (!stk.empty()){
curr = stk.top();
stk.pop();
cout << curr->data << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//this function will lead to the leafs
void leaf(Node* root){
if (root == NULL)
return;
stack<Node*> stc;
stc.push(root);
map<Node*, Node*> prnt;
prnt[root] = NULL;
while (!stc.empty()){
Node* curr = stc.top();
stc.pop();
if (!(curr->left) && !(curr->right))
calculatePath(curr, prnt);
if (curr->right){
prnt[curr->right] = curr;
stc.push(curr->right);
}
if (curr->left){
prnt[curr->left] = curr;
stc.push(curr->left);
}
}
}
int main(){
Node* root = newNode(67); //it will insert the nodes to create a tree
root->left = newNode(34);
root->right = newNode(89);
root->left->left = newNode(23);
root->left->right = newNode(95);
root->right->left = newNode(12);
leaf(root); //call the function leaf
return 0;
} কল করুন আউটপুট
যদি আমরা উপরের প্রোগ্রামটি চালাই তাহলে এটি নিম্নলিখিত আউটপুট তৈরি করবে
67 34 23 67 34 95 67 89 12


