n নোডের সাথে দেওয়া কাজটি হল একটি লিঙ্ক করা তালিকার শেষ থেকে nth নোডটি প্রিন্ট করা। প্রোগ্রামটি অবশ্যই একটি তালিকায় নোডের ক্রম পরিবর্তন করবে না বরং এটি শুধুমাত্র একটি লিঙ্ক করা তালিকার শেষ থেকে nth নোডটি প্রিন্ট করবে৷
উদাহরণ
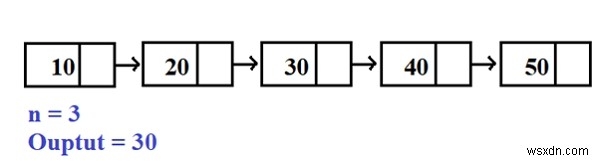
Input -: 10 20 30 40 50 60 N=3 Output -: 40
উপরের উদাহরণে, প্রথম নোড থেকে শুরু করে কাউন্ট-এন নোড পর্যন্ত নোডগুলি অতিক্রম করা হয় যেমন 10,20 30,40, 50,60 এবং শেষ থেকে তৃতীয় নোডটি হল 40৷
পুরো তালিকাটি অতিক্রম করার পরিবর্তে এই দক্ষ পদ্ধতিটি অনুসরণ করা যেতে পারে -
- একটি অস্থায়ী পয়েন্টার নিন, ধরা যাক, টেম্প অফ নোড
- এই টেম্প পয়েন্টারটিকে প্রথম নোডে সেট করুন যা হেড পয়েন্টার দ্বারা নির্দেশিত হয়
- একটি তালিকায় নোডের সংখ্যার কাউন্টার সেট করুন
- টেম্প থেকে টেম্পে সরান → পরবর্তী পর্যন্ত গণনা-এন
- প্রদর্শন তাপমাত্রা → ডেটা
যদি আমরা এই পদ্ধতিটি ব্যবহার করি, তাহলে গণনা 5 হবে এবং প্রোগ্রামটি 5-3 অর্থাৎ 2 পর্যন্ত লুপটি পুনরাবৃত্তি করবে, তাই 0 th এ 10 থেকে শুরু হচ্ছে 1 st -এ 20 এর চেয়ে অবস্থান 2 nd -এ অবস্থান এবং 30 অবস্থান যা ফলাফল। সুতরাং এই পদ্ধতির দ্বারা শেষ পর্যন্ত পুরো তালিকাটি অতিক্রম করার দরকার নেই যা স্থান এবং স্মৃতি সংরক্ষণ করবে।
অ্যালগরিদম
Start Step 1 -> create structure of a node and temp, next and head as pointer to a structure node struct node int data struct node *next, *head, *temp End Step 2 -> declare function to insert a node in a list void insert(int val) struct node* newnode = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)) newnode->data = val IF head= NULL set head = newnode set head->next = NULL End Else Set temp=head Loop While temp->next!=NULL Set temp=temp->next End Set newnode->next=NULL Set temp->next=newnode End Step 3 -> Declare a function to display list void display() IF head=NULL Print no node End Else Set temp=head Loop While temp!=NULL Print temp->data Set temp=temp->next End End Step 4 -> declare a function to find nth node from last of a linked list void last(int n) declare int product=1, i Set temp=head Loop For i=0 and i<count-n and i++ Set temp=temp->next End Print temp->data Step 5 -> in main() Create nodes using struct node* head = NULL Declare variable n as nth to 3 Call function insert(10) to insert a node Call display() to display the list Call last(n) to find nth node from last of a list Stop
উদাহরণ
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
//structure of a node
struct node{
int data;
struct node *next;
}*head,*temp;
int count=0;
//function for inserting nodes into a list
void insert(int val){
struct node* newnode = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newnode->data = val;
newnode->next = NULL;
if(head == NULL){
head = newnode;
temp = head;
count++;
} else {
temp->next=newnode;
temp=temp->next;
count++;
}
}
//function for displaying a list
void display(){
if(head==NULL)
printf("no node ");
else {
temp=head;
while(temp!=NULL) {
printf("%d ",temp->data);
temp=temp->next;
}
}
}
//function for finding 3rd node from the last of a linked list
void last(int n){
int i;
temp=head;
for(i=0;i<count-n;i++){
temp=temp->next;
}
printf("\n%drd node from the end of linked list is : %d" ,n,temp->data);
}
int main(){
//creating list
struct node* head = NULL;
int n=3;
//inserting elements into a list
insert(1);
insert(2);
insert(3);
insert(4);
insert(5);
insert(6);
//displaying the list
printf("\nlinked list is : ");
display();
//calling function for finding nth element in a list from last
last(n);
return 0;
} আউটপুট
linked list is : 1 2 3 4 5 6 3rd node from the end of linked list is : 4


